Abstract:
The 12th China National Conference on Computational Linguistics (CCL) will take place in Suzhou(http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Suzhou), China, 10-12 October 2013, hosted by Soochow University(http://www.suda.edu.cn). CCL, a bi-annual conference starting from 1991 and the flagship conference of the Chinese Information Processing Society (CIPS), the largest NLP scholar and expert community in China, is a premier nation-wide forum for disseminating new scholarly and technological work in computational linguistics, with major emphasis on computer processing of the languages in China, including Chinese and minority languages such as Tibetan, Mongolian and Uyghur.
Papers submitted to CCL can be in Chinese or English. Accepted papers in Chinese will be published in the Journal of Chinese Information Processing, the most influential Journal in Computational Linguistics in China, and accepted papers in English will be published by Springer in the Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence (LNAI) series.
Attached to the 12th CCL, we start up the First International Symposium on Natural Language Processing based on Naturally Annotated Big Data (1st NLP-NABD). NLP-NABD covers all the NLP topics, as listed above, with particular interest in the cutting edge methodologies and technologies of natural language processing in the era of big data. The so-called “naturally annotated” means different type of annotations on varieties of Web resources which are “unconsciously handcrafted” by Web users for their own purposes (in general, nothing to do with natural language processing), but can be used by computational linguists in a conscious and systematic way for various tasks of natural language processing, for examples, punctuation marks in Chinese can benefit word boundaries identification, social tags in social media can benefit keyword extraction, “categories” given in Wikipedia can benefit text categorization. The natural annotation can be explicit, as in above examples, or can be implicit, as “NOUN and other NPs” in “Beijing and other cities” as well as “NPs such as NOUN” in “cities such as Beijing”. This symposium aims at numerous research challenges ranging from very-large-scale unsupervised/semi-supervised machine leaning(deep learning for instance) of naturally annotated big data to integration of the learned resources and models with existing handcrafted “core” resources and “core” language computing models.
NLP-NABD targets at computation of any languages in the world. Only papers in English are accepted and will also be included in LNAI, together with the accepted English papers of 12th CCL.
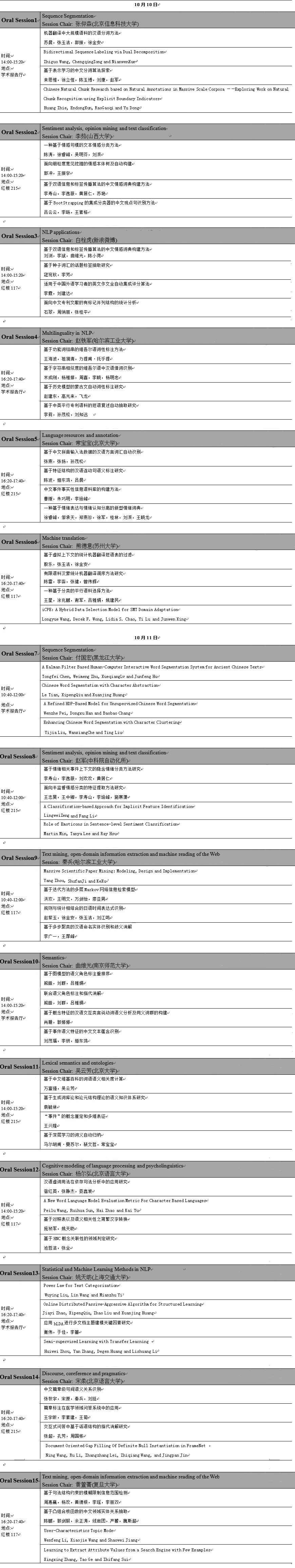
Oral
机器翻译中大规模语料的汉语分词方法
苏晨,张玉洁,郭振,徐金安
Bidirectional Sequence Labeling via Dual Decomposition
Zhiguo Wang, Chengqing Zong and Nianwen Xue
基于表示学习的中文分词算法探索
来思惟,徐立恒,陈玉博,刘康,赵军
Chinese Natural Chunk Research based on Natural Annotations in Massive Scale Corpora ——Exploring Work on Natural Chunk Recognition using Explicit Boundary Indicators
Huang Zhie, Endong Xun, Rao Gaoqi and Yu Dong
一种基于情感句模的文本情感分类方法
陈涛,徐睿峰,吴明芬,刘滨
面向细粒度意见挖掘的情感本体树及自动构建
郭冲,王振宇
基于双语信息和标签传播算法的中文情感词典构建方法
李寿山,李逸薇,黄居仁,苏艳
基于BootStrapping的集成分类器的中文观点句识别方法
吕云云,李旸,王素格
先秦词汇的时代特征自动获取及文献时代的自动判定
刘浏,李斌,曲维光,陈小荷
基于种子词汇的话题标签抽取研究
寇宛秋,李芳
适用于中国外语学习者的英文作文全自动集成评分算法
李霞,刘建达
面向中文专利文献的有标记并列结构的统计分析
石翠,周俏丽,张桂平
基于功能词缀串的维吾尔语词性标注方法
王海波,祖漪清,力提甫·托乎提
基于字符串相似度的维吾尔语中汉语借词识别
米成刚,杨雅婷,周喜,李晓,杨明忠
基于历史模型的蒙古文自动词性标注研究
赵建东,高光来,飞龙
基于中英平行专利语料的短语复述自动抽取研究
李莉,孙茂松,刘知远
基于中文拼音输入法数据的汉语方言词汇自动识别
张燕,张扬,孙茂松
基于特征结构的汉语连动句语义标注研究
陈波,姬东鸿,吕晨
中文事件事实性信息语料库的构建方法
曹媛,朱巧明,李培峰
一种基于情绪表达与情绪认知分离的新型情绪词典
徐睿峰,邹承天,郑燕珍,徐军,桂林,刘滨,王晓龙
基于虚拟上下文的统计机器翻译短语表的过滤
殷乐,张玉洁,徐金安
有限语料汉蒙统计机器翻译调序方法研究
陈雷,李淼,张健,曾伟辉
一种基于分类的平行语料选择方法
王星,涂兆鹏,谢军,吕雅娟,姚建民
iCPE: A Hybrid Data Selection Model for SMT Domain Adaptation
Longyue Wang, Derek F. Wong, Lidia S. Chao, Yi Lu and Junwen Xing
A Kalman Filter Based Human-Computer Interactive Word Segmentation System for Ancient Chinese Texts
Tongfei Chen, Weimeng Zhu, Xueqiang Lv and Junfeng Hu
Chinese Word Segmentation with Character Abstraction
Le Tian, Xipeng Qiu and Xuanjing Huang
A Refined HDP-Based Model for Unsupervised Chinese Word Segmentation
Wenzhe Pei,Dongxu Han and Baobao Chang
Enhancing Chinese Word Segmentation with Character Clustering
Yijia Liu, Wanxiang Che and Ting Liu
基于情绪相关事件上下文的隐含情绪分类方法研究
李寿山,李逸薇,刘欢欢,黄居仁
面向半监督情感分类的特征提取方法研究
王志昊,王中卿,李寿山,李培峰,施寒潇
A Classification-based Approach for Implicit Feature Identification
Lingwei Zeng and Fang Li
Role of Emoticons in Sentence-level Sentiment Classification
Martin Min, Tanya Lee and Ray Hsu
Massive Scientific Paper Mining: Modeling, Design and Implementation
Yang Zhou, Shufan Ji and Ke Xu
基于迭代方法的多层Markov网络信息检索模型
洪欢,王明文,万剑怡,廖亚男
规则与统计相结合的日语时间表达式识别
赵紫玉,徐金安,张玉洁,刘江鸣
基于多步聚类的汉语命名实体识别和歧义消解
李广一,王厚峰
基于图模型的语义角色标注重排序
熊皓,刘群,吕雅娟
联合语义角色标注和指代消解
熊皓,刘群,吕雅娟
基于概念特征的汉语交互类言说动词语义分析及同义词群的构建
肖珊,郭婷婷
基于事件语义特征的中文文本蕴含识别
刘茂福,李妍,姬东鸿
基于中文维基百科的词语语义相关度计算
万富强,吴云芳
基于生成词库论和论元结构理论的语义知识体系研究
袁毓林
“事件”的概念厘定和多维表征
王兴隆
基于深层学习的词义自动归纳
马尔胡甫·曼苏尔,裴文哲,常宝宝
汉语虚词用法在依存句法分析中的应用研究
昝红英,张静杰,娄鑫坡
A New Word Language Model Evaluation Metric For Character Based Languages
Peilu Wang, Ruihua Sun, Hai Zhao and Kai Yu
Automatic Discrimination of Pronunciations of Chinese Retroflex and Dental Affricates
Akemi Hoshino and Akio Yasuda
基于HNC概念关联性的领域判定研究
池哲洁,张全
Power Law for Text Categorization
Wuying Liu, Lin Wang and Mianzhu Yi
Online Distributed Passive-Aggressive Algorithm for Structured Learning
Jiayi Zhao, Xipeng Qiu, Zhao Liu and Xuanjing Huang
应用hLDA进行多文档主题建模关键因素研究
衡伟,于佳,李蕾
Semi-supervised Learning with Transfer Learning
Huiwei Zhou, Yan Zhang, Degen Huang and Lishuang Li
中文篇章级句间语义关系识别
张牧宇,宋原,秦兵,刘挺
篇章标注在医学领域问答系统中的应用
王宇昕,李素建,王荀
交互式问答中基于话语结构的指代消解研究
张超,孔芳,周国栋
Document Oriented Gap Filling Of Definite Null Instantiation in FrameNet
Ning Wang, Ru Li, Zhangzhang Lei, Zhiqiang Wang, and Jingpan Jin
基于句法结构约束的模糊限制信息范围检测
周惠巍,杨欢,黄德根,李瑶,李丽双
基于凸组合核函数的中文领域实体关系抽取
陈鹏,郭剑毅,余正涛,线岩团,严馨,魏斯超
User-Characteristics Topic Mode
Wenfeng Li, Xiaojie Wang and Shaowei Jiang
Learning to Extract Attribute Values from a Search Engine with Few Examples
Xingxing Zhang, Tao Ge and Zhifang Sui
基于对照表以及语义相关性之简繁汉字转换
庞祯军,姚天昉
Poster
Semantic Analysis of Chinese Prepositional Phrases for Patent Machine Translation
Renfen Hu, Yun Zhu and Yaohong Jin
Integrating Multi-source Bilingual Information for Chinese Word Segmentation in Statistical Machine Translation
Wei Chen, Wei Wei, Zhenbiao Chen and Bo Xu
Improving Chinese Word Segmentation Using Partially Annotated Sentences
Kaixu Zhang, Jinsong Su and Changle Zhou
HDP与互信息相结合的中文无指导分词
曹自强,李素建
Spies Hidden in Your Fans: An Effective Approach for Opinion Leader Discovery
Binyang Li, Kam-fai Wong, Lanjun Zhou
基于序列标注模型的情绪原因识别方法
李逸薇,李寿山,黄居仁,高伟
基于多特征融合的中文比较句识别算法
张辰,冯冲,刘全超,师超,黄河燕,周海云
蒙古文输入法输入码方案研究
白双成,张劲松,呼斯勒
基于统计翻译框架的蒙古文自动拼写校对方法
苏传捷,侯宏旭,杨萍,员华瑞
“把”字句的自动释义与句式变换研究
王璐璐,孙薇薇,袁毓林
基于语言模型解答大学生英语四级测试多选填空的实验性研究
范志航,林睿,杨沐昀,李生,赵铁军
中文短文本去重方法研究
高翔,李兵
Automatic Discrimination of Pronunciations of Chinese Retroflex and Dental Affricates
Akemi Hoshino and Akio Yasuda
融合音节特征的最大熵藏文词性标注研究
于洪志,李亚超,汪昆,冷本扎西
维哈柯及蒙语多文种语言相似性考查研究
达瓦·伊德木草,艾尼宛尔·托乎提,于清,吾守尔·斯拉木
基于机器翻译的跨语言关系抽取
胡亚楠,舒佳根,钱龙华,朱巧明
维吾尔语多词表达抽取方法研究
麦热哈巴·艾力,阿孜古丽·夏力甫,吐尔根·依布拉音
傣文自动分词系统的设计与实现
高廷丽,戴红亮
蒙古语熟语资源库的初步构建
海银花,那顺乌日图,额尔敦朝鲁
基于条件随机场的藏文人名识别研究
康才畯,龙从军,江荻
面向信息检索的藏文文本索引策略研究
万福成,何向真,夏建华,杜玉祥
基于规则的哈萨克语动词短语识别研究
古丽拉·阿东别克,古丽扎达·海沙
新闻语料中中日命名实体词汇翻译的自动抽取
尹存燕,黄书剑,戴新宇,陈家骏
中小学维吾尔语教材用词数据分析方法与应用研究
艾孜尔古丽,李晓,玉素甫.艾白都拉
多语料库中汉语四字格的切分和识别研究
徐润华,曲维光,陈小荷,王东波
基于词对依存分类的藏语树库半自动构建研究
华却才让,姜文斌,赵海兴,刘群
基于新闻语料库的越南语框架语义研究
林丽
上古汉语分词及词性标注语料库的构建——以《淮南子》为范例
留金腾,宋彦,夏飞
基于事件语义距离的V1-V2述结式判别研究
马腾,詹卫东
基于强制对齐的层次短语模型过滤和优化
付晓寅,魏玮,卢世祥,徐波
汉英篇章结构平行语料库的对齐标注研究
冯文贺
Graphic Language Model for Agglutinative Languages: Uyghur as Study Case
Miliwan Xuehelaiti, Kai Liu, Wenbin Jiang and Tuergen Yibulayin
Multi-Classifier Combination for Translation Error Detection
Jinhua Du, Junbo Guo, Sha Wang and Xiyuan Zhang
面向短语统计机器翻译的汉日联合分词研究
吴培昊,徐金安,张玉洁
汉英机器翻译中格式转换研究
刘智颖,郭艳波,晋耀红
Development of Traditional Mongolian Dependency Treebank
Xiangdong Su, Guanglai Gao and Xueliang
Chinese Sentence Compression: Corpus and Evaluation
Chunliang Zhang, Minghan Hu, Tong Xiao, Jingbo Zhu, Xue Jiang and Lixin Shi
个性化知识的表示方法
刘冬明,杨尔弘
基于句式结构的汉语图解析句法设计
彭炜明,宋继华,王宁
基于混合策略的汉语最长名词短语识别
钱小飞,侯敏
基于自动编码器的中文词汇特征无监督学习
张开旭,周昌乐
韩国语名词短结构特征分析及自动提取
安帅飞,毕玉德
藏语句法功能组块的边界识别
李琳,龙从军,江荻
评价短语的倾向性分析研究
侯敏,滕永林,陈毓麒
基于属性融合的微博用户分类模型
尹杰,张绍武,林鸿飞,魏现辉,刘晓霞
Emotional McGurk Effect? A Cross-Cultural Investigation on Emotion Expression under Vocal and Facial Conflict
Aijun Li, yuan Jia and Qiang Fang
Mining User Preferences for Recommendation: a Competition Perspective
Shaowei Jiang, Xiaojie Wang, Caixia Yuan and wenfeng li
Interactive Question Answering Based on FAQ
Song Liu, Yixin Zhong and Fuji Ren
年度新词语使用的时空分布考察
杨尔弘
基于图的查询日志实体别名抽取方法
石贝,孙乐,韩先培
Natural Language Understanding for Grading Essay Questions in Persian Language
Iman Mokhtari-Fard
“对象格”语义范畴及其相关语义角色的自动识别研究
汪梦翔,王厚峰
基于CCMO的现代汉语介词词义结构描写
邱庆山
基于语义关系图的词汇语义相关度计算研究
李佳媛,张仰森
现代汉语常用动词释义对比研究 --以《现代汉语词典》(第六版)和《“台湾教育部”教育部重编国语辞典(修订本)》为例
刘珺,徐德宽,陈淑梅
Exploiting Lexicalized Statistical Patterns in Chinese Linguistic Analysis
Yu Zhao and Maosong Sun
汉语自然话语的音高下倾
王茂林,訾广玲
歧义结构理解中的依存距离最小化倾向
赵怿怡,刘海涛
Interesting Linguistic Features in Coreference Annotation of an Inflectional Language
Maciej Ogrodniczuk, Katarzyna Głowińska, Mateusz Kope, Agata Savary and Magdalena Zawisławska
基于分词与词性标注的汉语逗号自动分类
古晶晶,周国栋
基于细粒度特征的话题句识别方法
蒋玉茹,宋柔
基于广义话题结构语料库的报告语体与小说语体对比研究
尚英,宋柔
基于LDA模型和SVM方法的微博用户性别判别
孙世杰,李珠峰,濮建忠
基于层次聚类的跨文本中文人名消歧研究
张菲菲,李宗海,周晓辉,李晓戈
一种抽取微博关键短语的网络图模型
黄河燕,廖黎姿,王亚珅,魏骁驰
微博语言的复杂网络特征研究
马宏炜,陆蓓,谌志群,黄孝喜,王荣波
基于中英文网络安全应用本体的跨语言信息检索研究
张飞,毕玉德
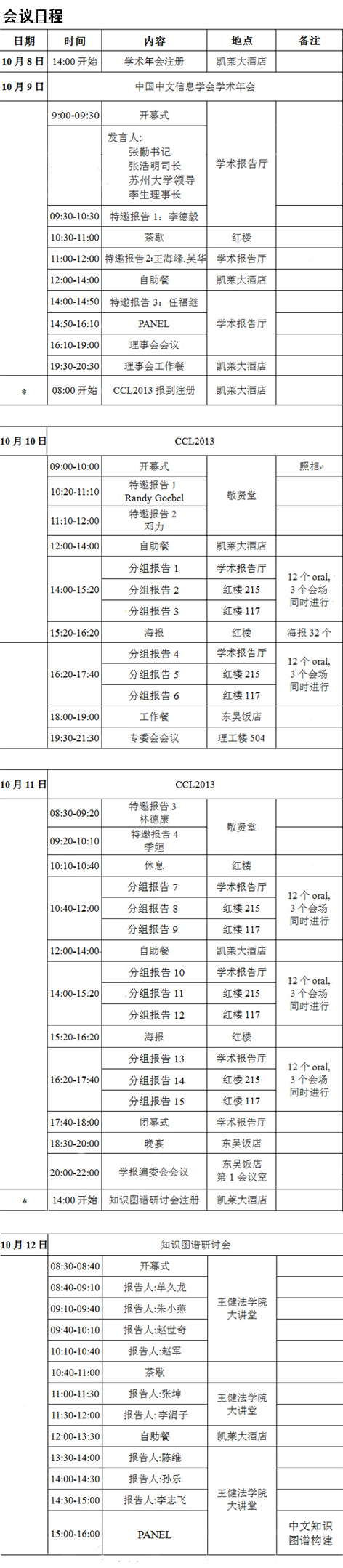
2013 Annual Meeting of China Association of
Chinese Information (CIPS 2013) and
The 12th National Conference on
Computational Linguistics (CCL 2013) Formal notice
Distinguished delegates: Hello everyone!
After the sixth director office meeting of the Seventh Council of China Chinese Information Society, Chinese Information Society Annual Meeting and Council (CIPS 2013) will be held in Soochow University in October 9, 2013.Chinese Information Processing (including Chinese and minority languages Information Processing) plays an important role in in the development of science technology and industry in the field of information technology development.The development of computer and Internet technology brings new challenge to Chinese information processing technology.Chinese information processing has become a new strategy of long-term development of information in science and technology.The academic years will be a majority of Chinese experts and scholars in the field of information processing (about 300 people) an event which will effectively promote the Chinese information processing field of theoretical innovation, research and technological exchanges and cooperation!We invite everyone to participate in Chinese Information Processing Society 2013 Annual Meeting to share, to discuss efforts to promote the field of Chinese information processing technology and industry innovation and development!The meeting's theme is:Depth learning and Chinese Information Processing.We will invite leading experts to do special reports, and conduct seminars related topics.
The Twelfth China National Conference on Computational Linguistics, CCL 2013 will be held October 10, 2013 -12 days held at the University in Suzhou.As the largest natural language processing experts community organizations - Chinese Information Processing Society (CIPS) is the flagship conference, the National Conference of Computational Linguistics from 1991 held biennially.CCL focuses on Chinese territory of various languages (such as Chinese, Tibetan, Mongolian and Uygur, etc.) calculation processing, computational linguistics for the dissemination of the latest academic and technical achievement provides a broad platform for the exchange.Meanwhile, "The First Big Data based on Natural Marked International Symposium on Natural Language Processing" (NLP-NABD 2013) will be held jointly with the CCL 2013.NLP-NABD pays special attention to big data era frontier of natural language processing methods and techniques and will focus on domestic and foreign large data based on the natural direction marked on a variety of cutting-edge research,including: How big natural label is valid for large-scale data unsupervised / semi-supervised machine learning (eg deep learning), how to learn to resources, models and existing manually labeled core resources and computational model combining the core language .
During the conference, Chinese Information Processing Society will hold the 1st Conference on Chinese Knowledge Graph.Knowledge Graph is the current academic and business research hotspot.Chinese Knowledge Map Construction for Chinese information processing and Chinese information retrieval has important value.The seminar will focus on mapping knowledge map construction of Chinese knowledge resources, technology, programs, policies, and issues and challenges to be studied, and promote research units as well as between the research community and industry, academic exchanges between, to explore the future large-scale Chinese knowledge map construction discussion and cooperation mechanisms.So far, the Assembly has been domestic natural language processing researchers' attention, currently has about 10 engaged in research and practice knowledge map famous universities, research institutions and business experts and academics who wish to participate and make a speech.
The meeting notice and meeting receipt send, please follow the notice on time to the designated locations and attend the meeting.
Firstly.The Meeting Time:
1. CIPS 2013: |
| Check in:At 14:00 on October 8th, 2013 |
| Begin:October 9, 2013(Lasting one day) |
2. CCL 2013 & NLP-NABD 2013: |
| Check in:At 8:00 on October 9th, 2013 |
| Begin: From October 10 to October 11(Lasting two days) |
3. Chinese Knowledge Graph: |
| Check in:At 14:00 on October 11th,2013 |
| Begin:October 12th,2013(Whole morning) |
| Conference Registration Location: 2013 Conference Group, CCL Kai Lai Hotel in Suzhou |
Secondly.The Meeting Rest Places:Kai Lai HOtel and Dongwu Hotel(600m far away outside the school),
coat paid by yourselves, the hotel coat standard in the receipt.
(Download receipt at the end of this page).
Thirdly.People participating in all meetings of the delegates goto the Kai Lai Hotel (meeting place of registration) to check in.
(Traffic Route is the Instructions-Route in this websides.
Fouth.Conference Registration Fee Situations:
| 1.Basic fee(for meeeting members): |
| Chinese Information Processing Society Annual Conference:member of a council(1000RMB per person),Not member of a council(500RMB per person). |
| Conference on Computational Linguistics:1000RMB per person. |
| Chinese Knowledge Graph:500RMB per person. |
| 2.Students at any conference can reduce 200RMB. |
| 3.If the representatives can participate in two meetings, the total coat will reduce 100RMB. And if the representatives can participate in three meetings, the total coat will reduce 200RMB. |
| 4.Non-Chinese Information Processing Society members at the expense of the delegates on the basis of the registration fee for each meeting an increase of 200 million. |
| 5.After September 20th or on-site payment delegate, each conference registration fee increase 200 yuan. |
Fifth.Conference registration fees shall be paid by the following ways:
| 1.Bank transfer. Account Name:中国中文信息学会.Bank:工商行北京市分行海淀西区支行.Account:0200004509014415619. |
| 2.The post office remittance. Payee:中国中文信息学会.Place:北京8718信箱"中国中文信息学会".Code:100190.Tel:010-62562916. |
| 3.Pay directly. Payee:中国中文信息学会.Place:北京海淀区中关村南四街4 Route院7 Route楼201房间.Tel:010-62562916. |
| 4.Pay at the scene. Suzhou Kai Lai Hotel 接待大厅会务组收费处. |
Note: please transfer (transfer) specified in the note "name (to attend the meeting number)", such as "Zhang San (1+2+3)"; many people together to transfer money please indicate the name, such as "Zhang San, Li Si, Wang Wu (1+2+3), or" respectively indicate the meeting number.
Sixth.Each paper accepted officially must have at least one author registered Conference on Computational Linguistics(CCL 2013 & NLP-NABD 2013),Otherwise, The paper will not be published.The publication costs of the organizing committee, notice.
seventh.Please fill in the receipt and write what you want to book a room type and accommodation dates clearly.Because during the meeting the shortage of accommodation, meeting receipt please in September 15th before sending to the business group e-mail: CCL2013@suda.edu.cn; Members who don't stay in the hotel still need to return the receipt. Please fill out each item of information, in order to Conference team prepare data, mail list, representative card etc.. Receive receipt, the business group will promptly return confirmation mail. If you do not receive the confirmation email, please contact the conference.
Eighth.Contact Methods:
| Longhua Qian:133-0620-8165 | qianlonghua@suda.edu.cn |
| Hongling Wang:138-6240-9198 | hlwang@suda.edu.cn |
| Yu Hong:133-7519-7289 | hongy@suda.edu.cn |
Ninth.Please note that this page tail meeting receipt download.
Greetings!
China Chinese Information Society
Aug,31th,2013
Meeting Receipt Download
CIPS2013 & CCL2013 Meeting Receipt.
Invited Speakers

Randy Goebel
University of Alberta, Canada
Topic:Natural Language Processing: The Challenge of Compressing Data to Models.
Summary:The problem of machine processing of natural language (NLP) has long been a research focus of artificial intelligence. This is partly because the use of natural language is easily conceived as a cognitive task requiring human-like intelligence. It is also because the rational structures for computer interpretation of language require the full suite of computational tools developed over the last hundred years (grammar, dictionaries, logic, parsing, inference, and context management). Most of the recent practical advances in NLP have arisen in the context of simple machine learning applied to large language corpora, to induce fragments of language models that provide the basis for interpretive and generative manipulation of language. These largely statistical models are arisen in what has been called the "pendulum swing" of NLP, in which statistical models have recently dominated those based on structural linguistics. In this lecture, we look at the concept of noisy corpora and their role in language models, including some interesting alternative sources of data for building language models. The applications range from complex language summary to the information extraction from medical, legal, and historical documents.
Resume:Randy Goebel is a professor in the department of Computing Science at the University of Alberta, in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada.
He is also vice president of the innovates Centre of Research Excellence (iCORE) at Alberta Innovates Technology Futures (AITF: www.albertainnovates.ca), chair of the Alberta Innovates Academy, and principle investigator in the Alberta Innovates Centre for Machine Learning (www.aicml.ca). He received the B.Sc. (Computer Science), M.Sc. (Computing Science), and Ph.D. (Computer Science) from the Universities of Regina, Alberta, and British Columbia, respectively.
At AITF, Randy is in charge of reshaping research investments (graduate student scholarships, research chairs, research centres). His research interests include applications of machine learning to systems biology, visualization, and web mining, as well as work on natural language processing, web semantics, and belief revision. Randy has experience working on industrial research projects in crew scheduling, pipeline scheduling, and steel mill scheduling, as well as scheduling and optimization projects for the energy industry in Alberta.
Randy has held appointments at the University of Waterloo, University of Tokyo, Multimedia University (Malaysia), Hokkaido University (Sapporo), and has had research collaborations with DFKI (German Research Centre for Artificial Intelligence), NICTA (National ICT Australia), RWC (Real World Computing project, Japan), ICOT (Institute for New Generation Computing, Japan), NII (National Institute for Informatics, Tokyo), and is actively involved in academic and industrial collaborative research projects in Canada, Australia, Europe, and China.

Dekang Lin
U.S. Google Inc.
Topic:Mining Lexical Knowledge from Unlabeled Text.
Summary:There has been a great deal work on acquiring lexical knowledge from unlabeled text, by using textual patterns to extract properties of words or phrases or relationships between them. Many types of lexical knowledge can be obtained this way, including the gender and animacy properties of words, type-instance relationships, part-of relationships, etc. In this talk, I will discuss several examples of this approach and address a number of related issues, such as ``What constitute good patterns?'', ``Where do they come from?'' and 'How to deal with the inherent noise in the extracted instances?''
Resume:Dekang Lin is a Staff Research Scientist at Google. Dekang Lin received his BSc from Tsinghua University and his PhD from the University of Alberta, both in Computer Science. Before joining Google in 2004, he was a professor at the University of Alberta. His main research interests include principle-based parsing and unsupervised learning from text and question-answering. He is Co-Editor-In-Chief of the Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics and was General Chair for ACL 2013 and Program Co-chair for ACL 2002.

Li Deng
U.S. Microsoft Research
Topic:Deep Learning: From Academic Concepts to Industrial Triumph.
Summary:Deep learning is a sub-field of machine learning that focuses on hierarchical representations of features or concepts, where high-level semantic-like features can emerge via automatic layer-by-layer learning from low-level features. In recent years, deep learning has achieved important successes in a variety of applied artificial intelligence tasks including speech recognition, computer vision, and natural language processing. The implications of such recent work have been prominently covered in recent media (e.g., NYT, Economist, MIT Technology Reviews, Google acquisition of DNNResearch, etc.). Since 2009, in partnership with leading academic researchers, Microsoft Research has been pursuing deep learning research and technology transfer, and has pioneered the development of industry-scale deep learning technology for speech recognition and other applications, resulting in industry-wide adoption of deep learning in Windows Phones (Microsoft), Android Phones (Google), iPhones (Siri of Apple and Nuance/IBM), and Baidu Phones. In this lecture, I will provide a historical overview on how academic conceptualization of deep learning rapidly evolved into wide product deployment worldwide within only a few short years, and discuss what implications this recent triumphant history may have for future academic-industrial collaborations. I will also go into some technical depth in describing the current deep learning technology, and in particular the disparate approaches which industry and academia take in current pursuits of the technology. I will conclude by analyzing future directions of deep learning, and speculating on what types of information processing and artificial intelligence applications may benefit most from deep learning technology in light of the known mechanisms of human brain that grounds intelligence and extreme effectiveness in information processing.
Resume:Li Deng received the Ph.D. degree from the University of Wisconsin-Madison. He was an assistant professor (1989-1992), tenured associate professor (1992-1996), and Full Professor (1996-1999) at the University of Waterloo, Ontario, Canada. In 1999, he joined Microsoft Research, Redmond, WA, where he is currently a Principal Researcher. Prior to MSR, he also worked or taught at Massachusetts Institute of Technology, ATR Interpreting Telecom. Research Lab. (Kyoto, Japan), and HKUST. He has been granted over 60 US or international patents in acoustics/audio, speech/language technology, and machine learning. He received numerous awards/honors bestowed by IEEE, ISCA, ASA, and Microsoft. In the general areas of audio/speech/language technology and science, machine learning, and signal/information processing, he has published over 300 refereed papers in leading journals and conferences and 4 books. He is a Fellow of the Acoustical Society of America (ASA), a Fellow of the IEEE, and a Fellow of the International Speech Communication Association (ISCA). He served on the Board of Governors of the IEEE Signal Processing Society (2008-2010), and as Editor-in-Chief for the IEEE Signal Processing Magazine (2009-2011). He serves as General Chair of the IEEE ICASSP-2013, and as Editor-in-Chief for the IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing. He initiated the deep learning work within Microsoft in 2009 (working with Prof. Geoff Hinton “in house”), with its inspiration and influence soon spread to the industry. His technical work and the leadership since 2009 in industry-scale deep learning with colleagues and academic collaborators have created significant impact in speech recognition and the related areas of information processing including information retrieval, spoken language understanding, speech synthesis, image recognition, machine translation, and web search.

Heng Ji
Computer Science Department
题目:Mining Lexical Knowledge from Unlabeled Text.
摘要:Recent years have witnessed a big data boom that includes a wide spectrum of heterogeneous unstructured data types, from image, speech, and multimedia signals to text documents. Information Extraction (IE) is a task of identifying “facts”, such as the attack/arrest events, people's jobs, people's whereabouts, merger and acquisition activity from such unstructured data sets on a massive scale. Traditional IE techniques assess the ability to extract information from individual documents in isolation. However, users need to gather information which may be scattered among a variety of sources. These facts may be redundant, complementary, incorrect or ambiguously worded. Furthermore, the extracted information from a document may need to augment an existing Knowledge Base (KB). This requires the ability to link events, entities and associated relations in a document to KB entries and thus present many unique challenges. In this talk, I will define several new extensions to state-of-the-art IE and systematically present the foundation, methodologies, algorithms, and implementations needed to create the next generation of information access with more accurate and robust extraction capabilities. More specifically, I will discuss: (1). How to break the performance ceiling of IE by changing the fundamental philosophy from sequential pipeline to joint modeling? (2). How to decode and encode information morphs from noisy data under active censorship? (3). How to construct and populate a trustable KB by marrying IE with data mining?
简历:Heng Ji is the Edward G. Hamilton Development Chair Associate Professor in Computer Science Department of Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI). She is a faculty member affiliated with three research centers at RPI: Tetherless World Constellation, Rensselaer Institute for Data Exploration and Applications, and Center for Cognition, Communication & Culture. She received her B.A. and M.A. in Computational Linguistics from Tsinghua University in 2000 and 2002 respectively; and her M.S. and Ph.D. in Computer Science from New York University in 2005 and 2007 respectively. Her research interests focus on Natural Language Processing, especially on Cross-source Information Extraction and Knowledge Base Population (KBP). She received Google Research Award, NSF CAREER award, Sloan Junior Faculty award, IBM Watson Faculty award, PACLIC2012 Best Paper Runner-up, "Best of SDM2013" Paper award and AI's Top 10 to Watch award by IEEE Intelligent Systems. She co-organized the NIST TAC-KBP track in 2010 and 2011, and served as the Information Extraction area chair for NAACL2012, ACL2013 and EMNLP2013. Her research is funded by NSF, ARL, DARPA, Google and IBM.
Traffic Routes
To a total of four Grand Hotel Da Kailai traffic routes, respectively, from the Suzhou North Station, Suzhou Station, Suzhou Industrial Park Station, Shanghai bus stops to Kai Lai Hotel.
Attention:Kai Lai Hotel is the meeting place of registration
Traffic routes 1:North Station to Kai Lai Hotel
Taxi
specific route:Sun Route,S227,Guanduli Interchange, Wanbao Square, East Central Route,Gan Jiang East Route.
Time:about 25 minutes
Cost:common taxi:about 47 yuan,call for taxi: 80-90yuan(call for taxi,Time:7:00-22:00,Tel:67776777)
Bus
Direct bus:
take 811 Route to Shuangta Station,walk 530m to Kai Lai Hotel.
Time:about 30 minutes
Cost:2 yuan per person
Take bus(the quickest):
take Express Line 8 Route air conditioning about 21 minutes,to Xiang Cheng Economic Development Zone Station,and take 89 Route about 31 minutes,to Xiangmen Station,240m walk to Kai Lai Hotel.
Time: About 20 minutes
Cost:4 yuan per person
Map:Blue line:taxi,Red line:Direct bus,Green line:Take bus.
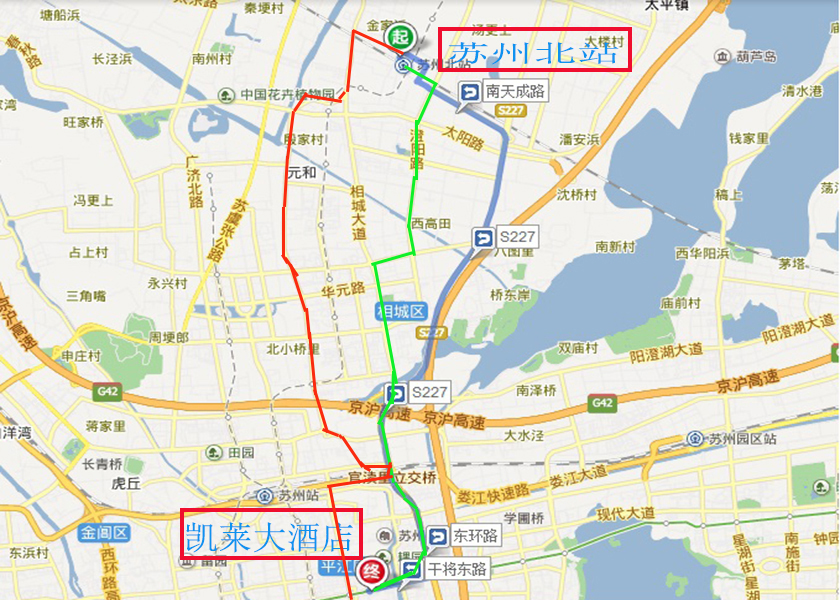
Suzhou North Station

taxi entrance

Bus Station

Traffic routes 2:Suzhou Station to Kai Lai Hotel
Taxi
Route1:specific route:Suzhou Station,North Temple Ta,People Route,White Ta North Route,Lingdun Route t oKai Lai Hotel.
Time:about 15 minutes
Cost:about 15 yuan
Route2:specific route:East Merge Route,Tong Fong Bay Bridge,Mo Ye Route,Gan Jiang East Route to Kai Lai Hotel.
Time:about 20 minutes
Cost:about 19 yuan(call for taxi,Time:7:00-22:00,Tel: 67776777)
Bus
Train Station South Square:
Direct 1(Relatively fast):take 40 Route about 40 minutes to Xiangmen Station,walk 240m to Kai Lai Hotel.
Time:about 40 minutes
Cost:2 yuan per person
Train Station North Square
Direct 2(Relatively fast)walk 170m to Train Station,take 518 about 18 minutes,at Xiangmen Station,walk 240m to Kai Lai Hotel.
Time:30 minutes
Cost:2 yuan per person
Deep blue line: taxi-Route 1,Light blue line: taxi-Route2,pink line: Direct1,Green line: Direct2.
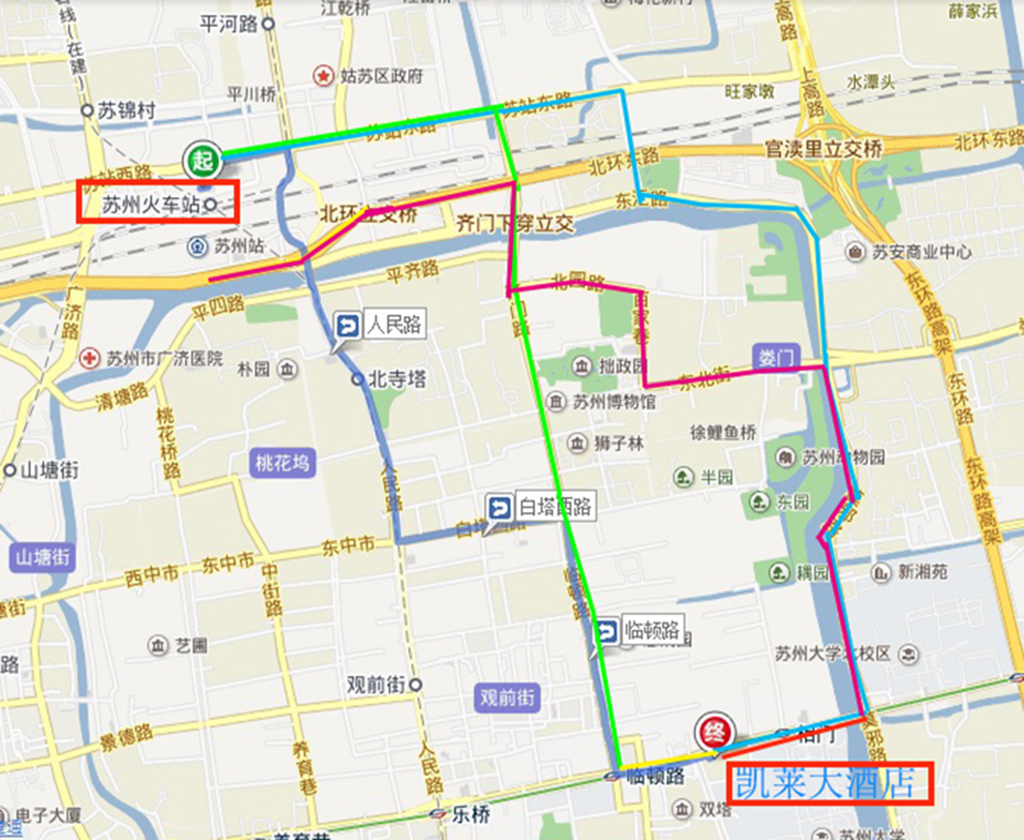
Suzhou Station

Train exit

Red arrow bus exit,Yellow arrow: taxi entrance

Traffic Route 3 Suzhou Park Station to Kai Lai Hotel
taxi:
Route 1:specific route:from Park Station,to He Xi Route,to He Xi Route Elevated,Su Hong Center Route,Bing Lang Route,Su Mu Route,New City Garden,Star Bling Route,Center New Route,Gan Jiang East Route,to Kai Lai Hotel.
Time:about 25 minutes
Cost:about 30 yuan(call for taxi,Time:7:00-22:00,Tel: 67776777)
bus:
No Direct
Take bus:take 139 or 115 about 17 minutes,to administrative center of Park Station West,walk 150m to Star Lake Station,take Subway 1 Route to Xiangmen,walk 240m to Kai Lai Hotel.
Time:about 50 minutes
Cost:5 yuan per person
Blue line:taxi,Green line:bus
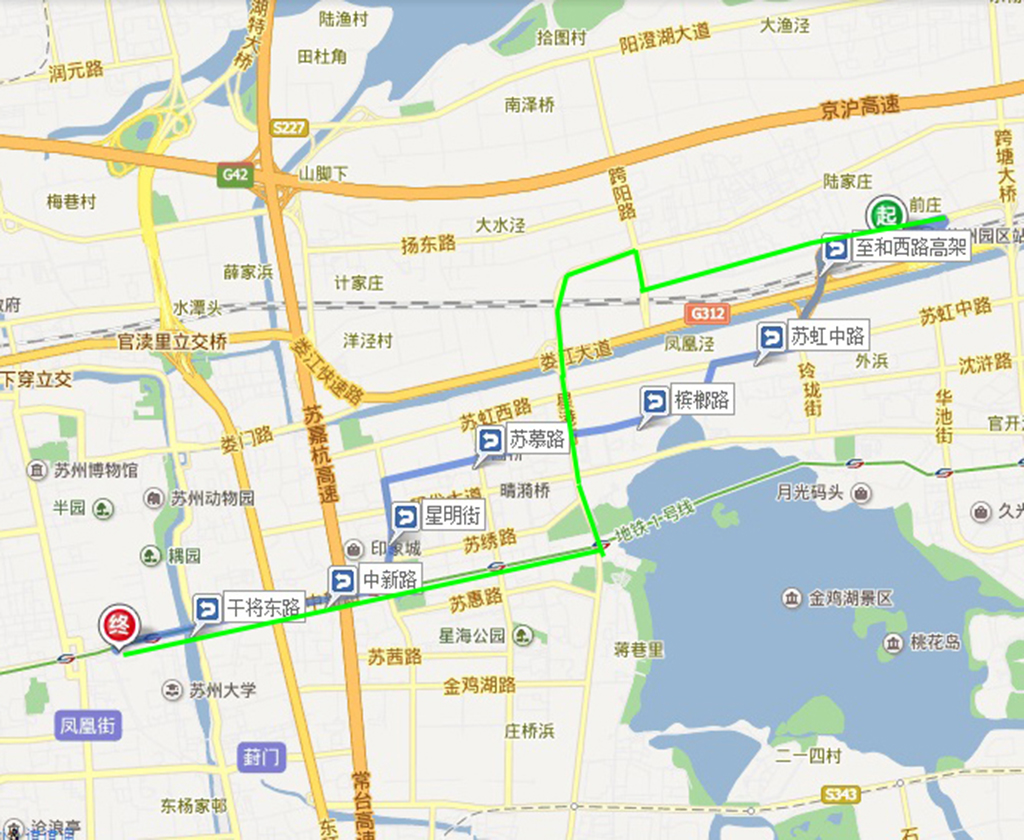
Suzhou Park Station

taxi exit

bus station

Traffic Route4 the shuttle from Shang Hai to Suzhou Kai Lai Hotel
Time:(Attention!!!)
Route1:Pudong to Suzhou
the earliest shuttle:10:10,30 minutes or 40 minutes per bus ,the last shuttle:20:40
Route2:Hongqiao to Suzhou
the earliest shuttle:11:10,30 minutes or 40 minutes per bus,the last shuttle:21:41
Parking Place:
Stopover:
taxi:
specific routeSuzhou Moon Route,Center Park,center New Route,Gan Jiang East Route,to Kai Lai Hotel.
Time:15 minutes
Cost:about 15 yuan(call for taxi,Time:7:00-22:00,Tel: 67776777)
bus:
walk to Impression of the city North Station,take 2 Route or 216 Route,to Xiangmen,walk 240m to Kai Lai Hotel.
Time:25 minutes
Cost:2 yuan per person
The end stop:Suzhou Bank(Lingdun Route)
taxi:
specific route: Gan Jiang East Route,lingdun Route to Kai Lai Hotel.
Time:2minutes
Cost:11yuan(call for taxi,Time:7:00-22:00,Tel: 67776777)
bus:
walk 100m to Yang Yuxiang Station,take 900 North road about 7 minutes to Xiangmen Station,walk 240m to Kai Lai Hotel.
Time:15 minutes
Cost:2 yuan per person
Subway:
subway1: Route lingdun Route to xiangmen,walk 240m to Kai Lai Hotel
Time:10 minutes
Cost:2 yuan per person
Back!!! Teachers and Students go to shang Hai Pudong,Hongqiao International airport.
Attention!
Suzhou Bus Station
Time:
the earliest shuttle:06:20,30minutes or 40minutes per bus,the last shuttle:17:00
Bus Station:Gan Jiang West Route 115 (the end stop:90m away from Suzhou Bank),
Red arrow:ticket office
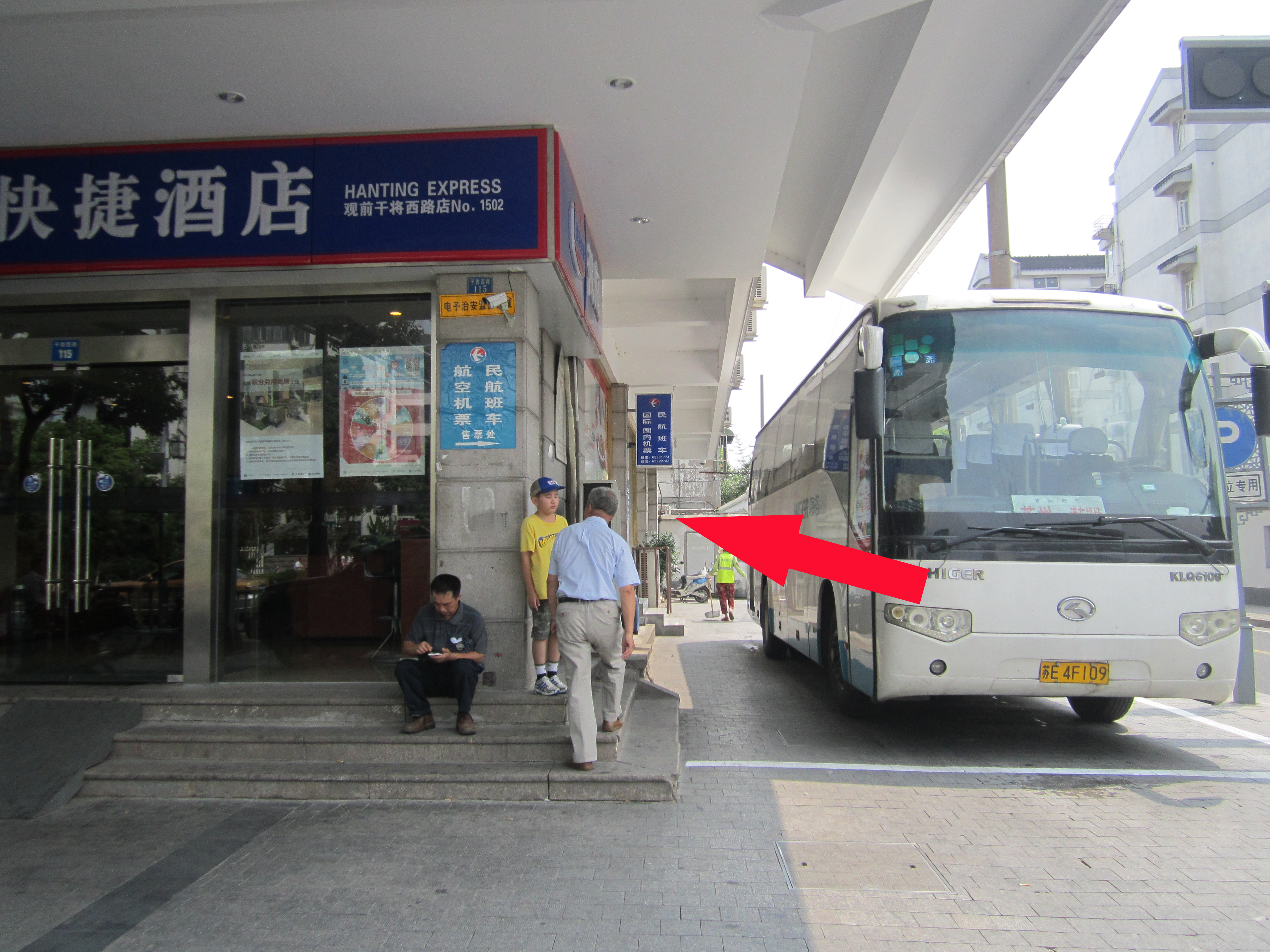

Shang Hai to Suzhou Stop(Beside Suzhou Bank)

lingdun Route Station Subway One Route